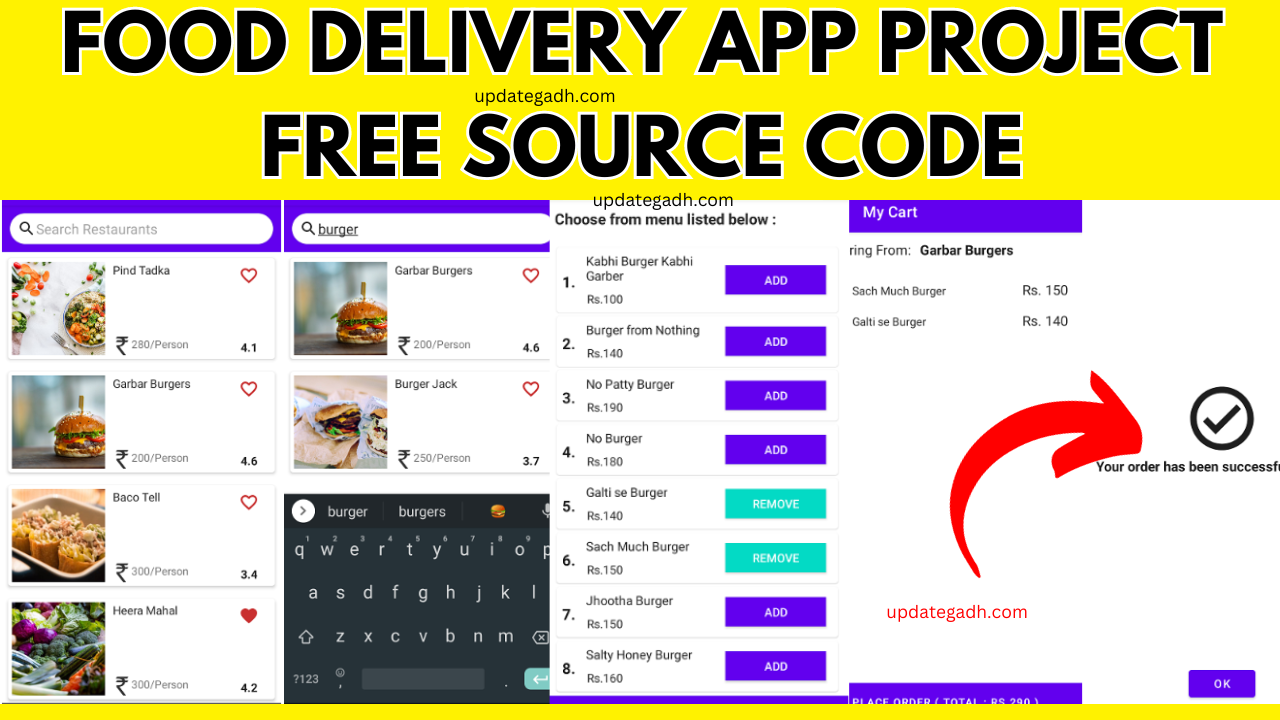
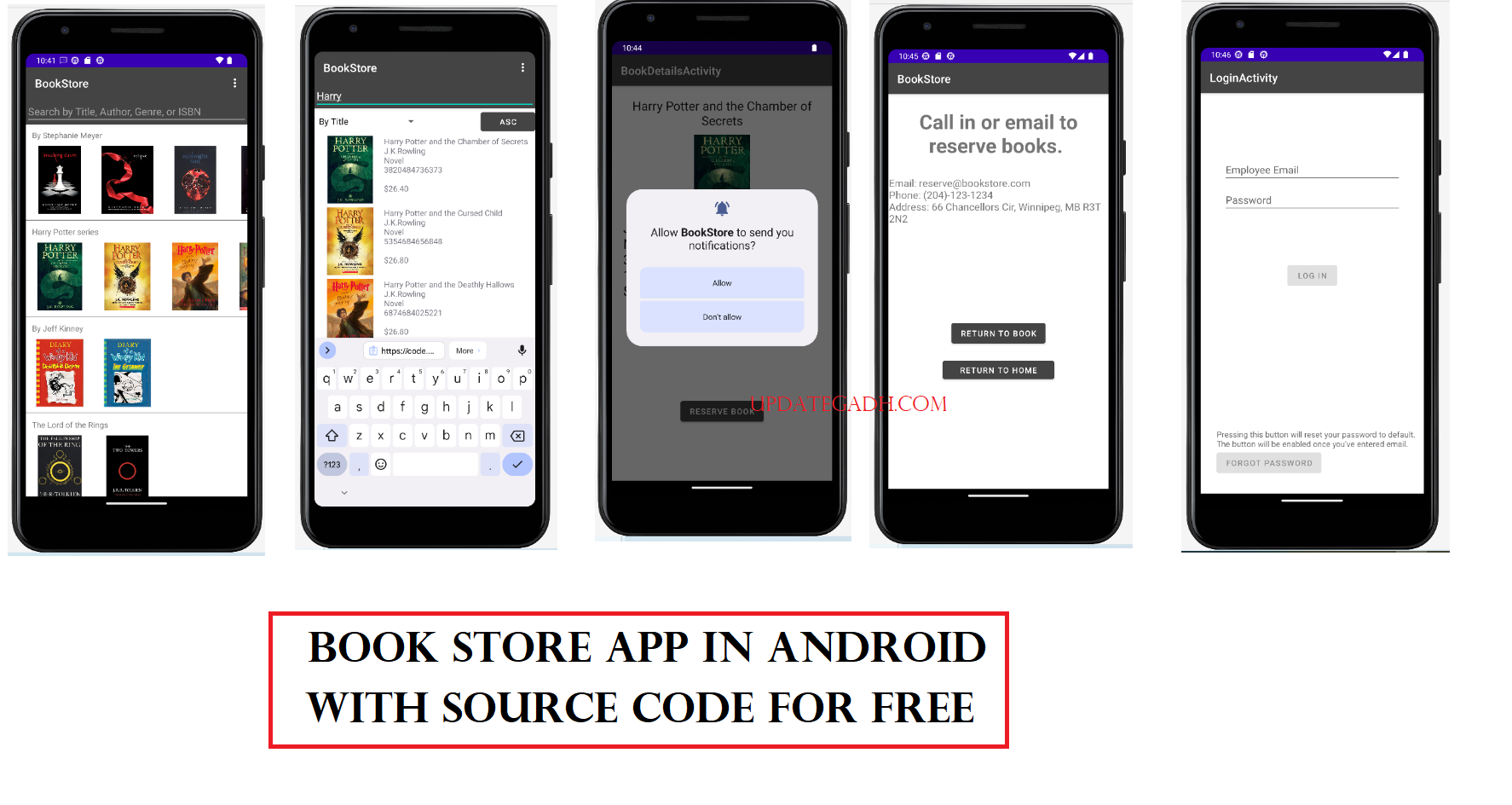
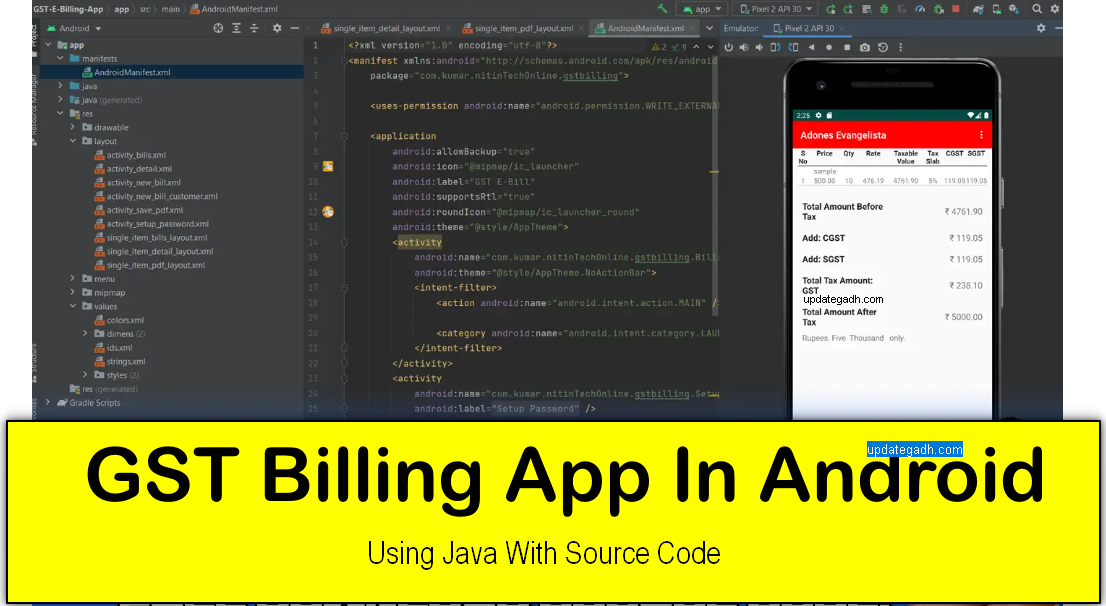
Creating a language Translator Application with Android Studio Free Source code
In an increasingly globalized world, language barriers are a significant challenge. This blog post will guide you through creating a language translator application using Android Studio, leveraging the power of machine learning and cloud APIs.
Table of Contents
Introduction
A language translator can convert text or speech from one language to another, facilitating communication between speakers of different languages. This tutorial will show you how to create a simple but powerful translate application using Android Studio, incorporating Google Translate API for accurate and efficient translations.
Prerequisites
Before we begin, ensure you have the following:
- Android Studio: The official IDE for Android development.
- Google Cloud Account: To access the Google Translate API.
- Basic Knowledge of Java/Kotlin: For Android app development.
Step 1: Setting Up Android Studio
- Install Android Studio:
Download ,install Android Studio (official website). - Create a New Project:
Open Android Studio and start a new project. Select “Empty Activity” and provide the necessary details (project name, package name, etc.).
Step 2: Setting Up Google Translate API
- Enable Google Translate API:
- Go to the Google Cloud Console.
- Create a new project.
- Navigate to the API Library and enable the Google Cloud Translation API.
- Create API Key:
Step 3: Adding Dependencies
Open your build.gradle file (app level) and add the following dependencies:
dependencies {
implementation 'com.google.cloud:google-cloud-translate:1.94.1'
implementation 'com.android.volley:volley:1.2.0'
}Sync your project to ensure all dependencies are correctly added.
Step 4: Designing the User Interface
- Open
activity_main.xml:
- Add an
EditTextfor the input text. - Add a
Spinnerfor selecting the target language. - Add a
Buttonfor triggering the translation. - Add a
TextViewfor displaying the translated text.
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="16dp">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/inputText"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="Enter text to translate" />
<Spinner
android:id="@+id/languageSpinner"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/translateButton"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Translate" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/translatedText"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="16dp" />
</LinearLayout>Step 5: Implementing Translation Logic
- Initialize Google Translate API:
In yourMainActivity.java, initialize the Google Translate API using the API key.
import com.android.volley.Request;
import com.android.volley.RequestQueue;
import com.android.volley.Response;
import com.android.volley.VolleyError;
import com.android.volley.toolbox.StringRequest;
import com.android.volley.toolbox.Volley;
import org.json.JSONException;
import org.json.JSONObject;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private EditText inputText;
private Spinner languageSpinner;
private TextView translatedText;
private String apiKey = "YOUR_API_KEY";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
inputText = findViewById(R.id.inputText);
languageSpinner = findViewById(R.id.languageSpinner);
translatedText = findViewById(R.id.translatedText);
findViewById(R.id.translateButton).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
translateText();
}
});
setupLanguageSpinner();
}
private void setupLanguageSpinner() {
// Populate the spinner with a list of languages
}
private void translateText() {
String text = inputText.getText().toString();
String targetLanguage = languageSpinner.getSelectedItem().toString();
String url = "https://translation.googleapis.com/language/translate/v2?key=" + apiKey +
"&q=" + text + "&target=" + targetLanguage;
RequestQueue queue = Volley.newRequestQueue(this);
StringRequest stringRequest = new StringRequest(Request.Method.GET, url,
new Response.Listener<String>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(String response) {
try {
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(response);
String translatedTextStr = jsonObject.getJSONArray("data")
.getJSONObject(0)
.getJSONArray("translations")
.getJSONObject(0)
.getString("translatedText");
translatedText.setText(translatedTextStr);
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, new Response.ErrorListener() {
@Override
public void onErrorResponse(VolleyError error) {
translatedText.setText("Translation failed!");
}
});
queue.add(stringRequest);
}
}Step 6: Testing the Application
- Run the Application:
- Connect your Android device.
- Run the application from Android Studio.
- Enter text, select the target language, and click the translate button to see the translated text.
Outputs
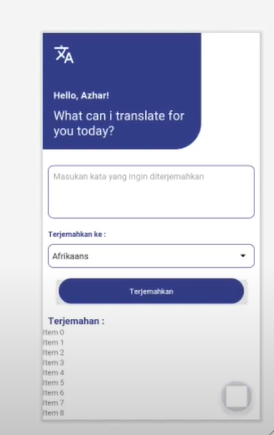
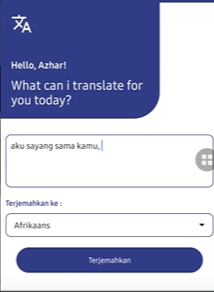
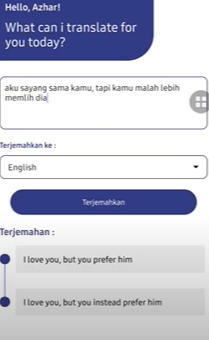
Step 7: Download Source Code
👇Project Price Details Click Below 👇
- Complete Python Course : Click here
- Free Notes :- Click here
- New Project :-https://www.youtube.com/@Decodeit2
- How to setup this Project Complete video – Click here
Conclusion
Creating a language translator application with Android Studio is a great way to understand the integration of cloud APIs with mobile applications. This project not only enhances your Android development skills but also gives you hands-on experience with real-time translation services.
Tags and SEO
Tags:
- Android Development
- Translate Application
- Google Translate API
- Mobile App Development
- Android Studio