Join Operations in SQL
Data often resides in multiple tables in databases, and combining this data effectively is crucial for meaningful insights. SQL join operations are useful in this situation. Rows from two or more tables can be combined by using a common column. In this blog, we’ll explore join operations using an example in Python with MySQL, explained in a professional yet approachable tone.
Download New Real Time Projects :-Click here
Creating Tables
Let’s begin by creating a new table, Departments, alongside an existing Employee table.
CREATE TABLE Departments (
Dept_id INT(20) PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
Dept_Name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL
);
Now, insert some values into the Departments table:
INSERT INTO Departments VALUES (201, 'CS');
INSERT INTO Departments VALUES (202, 'IT');
Similarly, ensure the Employee table contains relevant records with a column Dept_id to match the department details.
Join Operations in Action
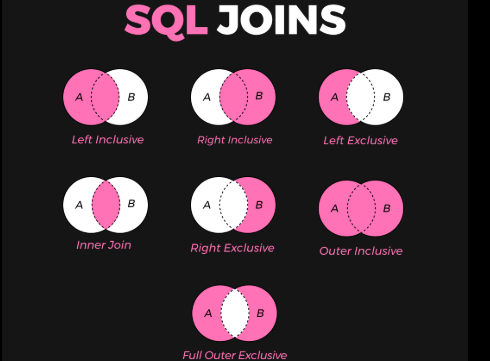
Inner Join
The Inner Join retrieves records matching a condition in both tables. Here, we’ll fetch employee details along with their department names using the common column Dept_id.
Python Code for Inner Join
import mysql.connector
# Create the connection object
myconn = mysql.connector.connect(
host="localhost", user="root", passwd="yourpassword", database="PythonDB"
)
# Create the cursor object
cur = myconn.cursor()
try:
# Join query
cur.execute("""
SELECT Employee.id, Employee.name, Employee.salary,
Departments.Dept_id, Departments.Dept_Name
FROM Departments
JOIN Employee ON Departments.Dept_id = Employee.Dept_id
""")
print("ID Name Salary Dept_Id Dept_Name")
for row in cur:
print(f"{row[0]} {row[1]} {row[2]} {row[3]} {row[4]}")
except Exception as e:
print("Error:", e)
myconn.rollback()
myconn.close()
Output:
| ID | Name | Salary | Dept_Id | Dept_Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 | John | 25000 | 201 | CS |
| 103 | David | 25000 | 202 | IT |
Right Join
The Right Join includes all records from the right table (Employee) and matching records from the left table (Departments). It helps identify employees without a department.
To demonstrate, let’s add a record for an employee who doesn’t belong to any department:
INSERT INTO Employee (id, name, salary, branch_name)
VALUES (108, 'Alex', 29900, 'Mumbai');
Python Code for Right Join
try:
cur.execute("""
SELECT Employee.id, Employee.name, Employee.salary,
Departments.Dept_id, Departments.Dept_Name
FROM Departments
RIGHT JOIN Employee ON Departments.Dept_id = Employee.Dept_id
""")
print("ID Name Salary Dept_Id Dept_Name")
for row in cur:
print(f"{row[0]} {row[1]} {row[2]} {row[3]} {row[4]}")
except Exception as e:
print("Error:", e)
myconn.rollback()
myconn.close()
Output:
| ID | Name | Salary | Dept_Id | Dept_Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 | John | 25000 | 201 | CS |
| 108 | Alex | 29900 | NULL | NULL |
Left Join
The Left Join includes all records from the left table (Departments) and matching records from the right table (Employee). It ensures no department data is missed.
Python Code for Left Join
try:
cur.execute("""
SELECT Employee.id, Employee.name, Employee.salary,
Departments.Dept_id, Departments.Dept_Name
FROM Departments
LEFT JOIN Employee ON Departments.Dept_id = Employee.Dept_id
""")
print("ID Name Salary Dept_Id Dept_Name")
for row in cur:
print(f"{row[0]} {row[1]} {row[2]} {row[3]} {row[4]}")
except Exception as e:
print("Error:", e)
myconn.rollback()
myconn.close()
Output:
| Dept_Id | Dept_Name | ID | Name | Salary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 201 | CS | 101 | John | 25000 |
| 202 | IT | 103 | David | 25000 |
PHP PROJECT:- CLICK HERE
joins in sql with examples
self join in sql
types of joins in sql
cross join in sql
sql join 3 tables
inner join in sql
natural join in sql
left join in sql
Join Operations in SQL
set operations in sql
aggregate functions in sql
join operations in sql w3schools
join operations in sql server
join operations in sql oracle
join operations in sql server with example
Join Operations in SQL with Python
🎓 Need Complete Final Year Project?
Get Source Code + Report + PPT + Viva Questions (Instant Access)
🛒 Visit UpdateGadh Store →