Scientific Calculator in Python
In today’s fast-paced world, the need for a comprehensive and powerful scientific calculator has become essential. Whether you’re a student working on a complex math problem or a professional handling scientific data, a good calculator saves time and effort. We’ll walk you through building your own Python scientific calculator with a graphical user interface (GUI) in this blog article. This project combines simplicity with functionality, making it a great addition to any coder’s toolkit.
Why Build a Scientific Calculator?
Programming a scientific calculator from scratch is an excellent way to understand mathematical operations, GUI development, and the versatility of Python. This project is a perfect fit for those looking to:
- Use Python’s well-known Tkinter toolkit to learn GUI development.
- Enhance problem-solving skills through coding complex functions like trigonometry, logarithms, and more.
- Prepare for real-world projects where similar logic and interface skills are required.
Let’s get started on building a professional yet intuitive calculator that handles basic arithmetic operations and scientific calculations!
Download New Real Time Projects :-Click here
Tools and Libraries
- Python 3.x: The latest version of Python.
- Tkinter: A built-in Python package for graphical user interface development.
You can install Python here.
Key Features
- Basic Operations: Addition, subtraction, multiplication, division.
- Advanced Functions: Trigonometric functions (sin, cos, tan), logarithms, exponents, square root, and more.
- Error Handling: Stops crashes brought on by erroneous input.
https://updategadh.com/category/php-project
Setting Up the Project
Let’s start by building the fundamental framework of our application and importing the required components.
import tkinter as tk
import math
# Initialize the main window
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("Scientific Calculator")
root.geometry("400x600")
# Global variable for storing the input expression
expression = ""Building the User Interface
The Tkinter library makes it easy to build a simple interface with buttons for numbers, operations, and scientific functions. Here’s how we can lay out the buttons and display:
# Function to update the input field
def press(num):
global expression
expression += str(num)
equation.set(expression)
# Function to evaluate the final expression
def evaluate():
try:
global expression
result = str(eval(expression)) # Evaluate the expression
equation.set(result)
expression = result
except:
equation.set("error")
expression = ""
# Function to clear the input field
def clear():
global expression
expression = ""
equation.set("")
# Input field where the expression will be displayed
equation = tk.StringVar()
input_field = tk.Entry(root, textvariable=equation, font=('Arial', 20), bd=8, relief='ridge', justify='right')
input_field.grid(row=0, column=0, columnspan=4)Adding Buttons
Next, let’s create the buttons for numbers, basic operations, and scientific functions. We’ll also implement the corresponding functionality.
# Creating buttons for numbers and basic operators
buttons = [
'7', '8', '9', '/', 'C',
'4', '5', '6', '*', '(',
'1', '2', '3', '-', ')',
'0', '.', '=', '+', 'sqrt'
]
row_value = 1
col_value = 0
for button in buttons:
if button == '=':
tk.Button(root, text=button, height=2, width=7, command=evaluate).grid(row=row_value, column=col_value)
elif button == 'C':
tk.Button(root, text=button, height=2, width=7, command=clear).grid(row=row_value, column=col_value)
elif button == 'sqrt':
tk.Button(root, text=button, height=2, width=7, command=lambda: press('math.sqrt(')).grid(row=row_value, column=col_value)
else:
tk.Button(root, text=button, height=2, width=7, command=lambda x=button: press(x)).grid(row=row_value, column=col_value)
col_value += 1
if col_value > 4:
col_value = 0
row_value += 1Adding Scientific Functions
In a scientific calculator, you’ll need to add more complex mathematical functions. These include trigonometric calculations (sin, cos, tan), logarithms, and exponents. Here’s how to handle them:
# Function to add advanced scientific functionalities
def add_scientific_buttons():
scientific_buttons = [
('sin', lambda: press('math.sin(')),
('cos', lambda: press('math.cos(')),
('tan', lambda: press('math.tan(')),
('log', lambda: press('math.log(')),
('exp', lambda: press('math.exp('))
]
for i, (text, command) in enumerate(scientific_buttons):
tk.Button(root, text=text, height=2, width=7, command=command).grid(row=row_value+i, column=5)
add_scientific_buttons()Running the Calculator
Finally, you can run your application and see the calculator in action:
# Main event loop to run the application
root.mainloop()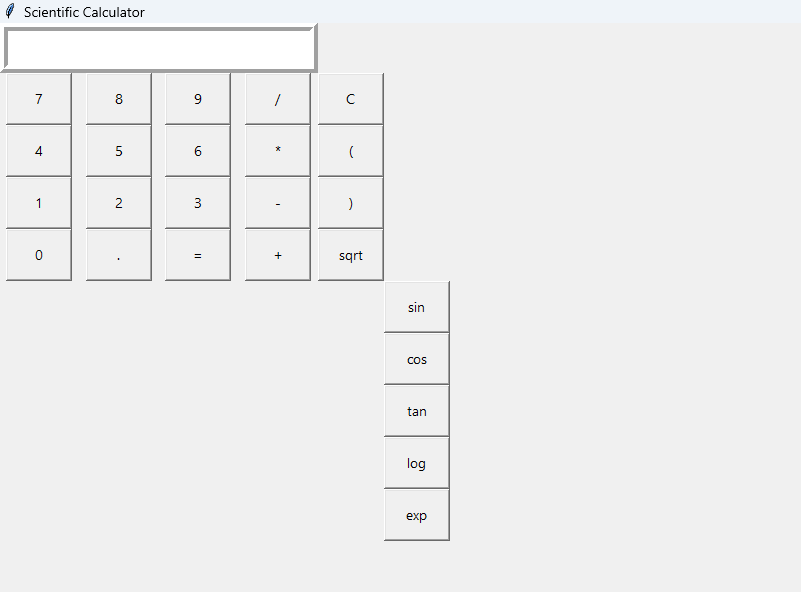
- scientific calculator in python with source code pdf
- simple scientific calculator in python with source code
- scientific calculator in python with source code github
- scientific calculator in python with source code free download
- scientific calculator in python without gui
- project report on scientific calculator in python pdf
- scientific calculator in python code
- scientific-calculator python github
🎓 Need Complete Final Year Project?
Get Source Code + Report + PPT + Viva Questions (Instant Access)
🛒 Visit UpdateGadh Store →